Contents
- I. Introduction
- II. Anatomy of the Dog Nervous System
- III. Functions of the Dog Nervous System
- IV. Dog Behavior and the Nervous System
- V. Common Nervous System Disorders in Dogs
- VI. Training and Enrichment for a Healthy Nervous System in Dogs
- VII. Nutrition and Supplements for Optimal Nervous System Function in Dogs
I. Introduction
The nervous system of a dog plays a crucial role in controlling its behavior and movement. It is a complex network of nerves, cells, and tissues that allows dogs to perceive and respond to their environment. Understanding how the dog’s nervous system functions can help dog owners better care for their furry companions.
Dogs, like humans, have a central nervous system (CNS) and a peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord, while the PNS includes the nerves that extend throughout the body. These two systems work together to coordinate the dog’s actions and responses.
The dog’s brain is responsible for processing sensory information, such as sight, sound, and smell, and initiating appropriate responses. It controls vital functions like breathing, heart rate, and digestion. The spinal cord acts as a communication highway, transmitting signals between the brain and the rest of the body.
The PNS consists of sensory and motor nerves. Sensory nerves carry information from the body to the brain, allowing the dog to perceive its surroundings. Motor nerves, on the other hand, transmit signals from the brain to the muscles, enabling movement.
Throughout this article, we will delve deeper into the intricacies of the dog’s nervous system. We will explore how it influences behavior and movement, shedding light on the fascinating ways in which dogs interact with their environment. By gaining a better understanding of the dog’s nervous system, we can provide them with the care and attention they need to lead happy and healthy lives.
II. Anatomy of the Dog Nervous System
The dog nervous system is a complex network of cells and tissues that controls behavior and movement. It can be divided into two main parts: the Central Nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
A. Central Nervous System (CNS)
The Central Nervous System consists of the brain and spinal cord. It is responsible for processing and coordinating information received from the body and sending out appropriate responses.
1. Brain
The brain is the command center of the nervous system. It controls all bodily functions and processes sensory information. The dog’s brain is similar to the human brain, but with some differences in size and structure.
a. Cerebrum
The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain and is responsible for higher cognitive functions such as learning, memory, and problem-solving. It is divided into two hemispheres, each controlling the opposite side of the body.
b. Cerebellum
The cerebellum is located at the back of the brain and is responsible for coordinating movement, balance, and posture. It receives information from the sensory systems, spinal cord, and other parts of the brain to ensure smooth and coordinated movement.
c. Brainstem
The brainstem is the lower part of the brain that connects the brain to the spinal cord. It controls basic functions such as breathing, heart rate, and digestion. It also serves as a pathway for information to and from the brain.
2. Spinal Cord
The spinal cord is a long, tubular structure that runs from the base of the brain to the lower back. It serves as a communication pathway between the brain and the rest of the body. The spinal cord is responsible for transmitting sensory information from the body to the brain and motor commands from the brain to the body.
B. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
The Peripheral Nervous System consists of nerves and ganglia that extend from the CNS to the rest of the body. It connects the CNS to the limbs, organs, and other body parts, allowing for communication and control.
1. Nerves
Nerves are bundles of fibers that transmit signals between the CNS and the body. They carry sensory information from the body to the brain and motor commands from the brain to the body. Nerves can be classified into different types based on their function and location.
2. Ganglia
Ganglia are clusters of nerve cell bodies located outside the CNS. They are involved in the processing and integration of sensory information. Ganglia can be found along the spinal cord and in various parts of the body.
III. Functions of the Dog Nervous System
The dog nervous system plays a crucial role in controlling behavior and movement. It consists of various components that work together to ensure the dog can perceive the environment, respond to stimuli, and coordinate motor responses. In this section, we will explore the three main functions of the dog nervous system: sensory function, motor function, and integration function.
A. Sensory Function
1. How dogs perceive the environment through their senses
Dogs have a remarkable ability to perceive the world around them through their senses. Their sense of smell is particularly powerful, with over 220 million olfactory receptors compared to humans’ mere 5 million. This heightened sense of smell allows dogs to detect scents that are undetectable to humans, making them excellent trackers and search and rescue animals.
In addition to their sense of smell, dogs also rely on their sense of sight, hearing, taste, and touch to gather information about their surroundings. Their eyesight, although not as sharp as humans, is adapted for detecting movement and low-light conditions. Dogs can hear frequencies that are beyond the range of human hearing, enabling them to detect sounds from a distance. Their taste buds are less sensitive compared to humans, but they can still distinguish between different flavors. Lastly, dogs have a highly developed sense of touch, which allows them to feel vibrations and textures.
2. Role of sensory neurons in transmitting information to the CNS
Sensory neurons are responsible for transmitting information from the dog’s senses to the central nervous system (CNS). These specialized cells convert sensory stimuli into electrical signals that can be understood by the CNS. Once the sensory information reaches the CNS, it is processed and interpreted, leading to appropriate responses and behaviors.
B. Motor Function
1. How the nervous system controls voluntary and involuntary movements in dogs
The dog’s nervous system controls both voluntary and involuntary movements. Voluntary movements are those that the dog consciously initiates, such as walking, running, or jumping. These movements are coordinated by the motor cortex in the brain, which sends signals to the muscles through motor neurons.
Involuntary movements, on the other hand, are automatic and not under conscious control. They include reflexes, such as blinking or withdrawing a paw from a hot surface, as well as vital functions like heartbeat and digestion. These movements are regulated by the autonomic nervous system, which consists of the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions.
2. Role of motor neurons in transmitting signals from the CNS to muscles and glands
Motor neurons play a crucial role in transmitting signals from the CNS to the muscles and glands in the dog’s body. These specialized cells carry the electrical impulses generated by the CNS to the target tissues, allowing for coordinated movement and responses. Motor neurons innervate skeletal muscles, controlling voluntary movements, as well as smooth muscles and glands, regulating involuntary functions.
C. Integration Function
1. How the nervous system integrates sensory information and coordinates motor responses
The integration function of the dog nervous system involves processing and integrating sensory information from the environment and coordinating appropriate motor responses. This complex process takes place in the brain and spinal cord, which form the central nervous system.
When sensory information reaches the CNS, it is analyzed, interpreted, and compared to existing knowledge and experiences. This integration allows the dog to make sense of the environment and respond accordingly. For example, if a dog sees a ball rolling towards it, the visual information is integrated with past experiences, and the motor response of catching the ball is coordinated.
2. Importance of integration for normal behavior and movement in dogs
Integration is crucial for normal behavior and movement in dogs. It allows them to navigate their surroundings, interact with other animals and humans, and perform various tasks. Without proper integration of sensory information, dogs may exhibit abnormal behaviors or have difficulty coordinating movements.
For example, a dog with a sensory integration disorder may become easily overwhelmed by sensory stimuli, leading to anxiety or aggression. Similarly, a dog with a motor integration disorder may have trouble coordinating movements, resulting in clumsiness or difficulty performing complex tasks.
IV. Dog Behavior and the Nervous System
Understanding the relationship between the nervous system and behavior in dogs is crucial for dog owners and trainers alike. The nervous system plays a vital role in influencing a dog’s behavior, including their instinctive behaviors, learned behaviors, and emotional responses. Let’s delve deeper into how the nervous system impacts dog behavior.
A. Relationship between the nervous system and behavior in dogs
The nervous system is responsible for transmitting signals throughout a dog’s body, enabling them to respond to various stimuli and engage in different behaviors. It consists of the central nervous system (CNS), which includes the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system (PNS), which comprises the nerves that extend throughout the body.
In dogs, the nervous system and behavior are intricately connected. The brain processes information received from the environment and sends signals to the body, resulting in specific behaviors. The PNS acts as a communication network, relaying information between the brain and the rest of the body.
B. How the nervous system influences dog behavior
1. Instinctive behaviors:
Dogs exhibit a range of instinctive behaviors that are hardwired into their genetic makeup. These behaviors are essential for their survival and include activities such as hunting, mating, and territorial marking. The nervous system plays a crucial role in coordinating these instinctive behaviors.
For example, when a dog spots prey, the visual information is processed by the brain, which then triggers a series of responses through the nervous system. The dog’s muscles tense, their heart rate increases, and they may start to stalk or chase the prey. These instinctive behaviors are controlled by specific regions of the brain and the corresponding neural pathways.
2. Learned behaviors:
In addition to instinctive behaviors, dogs also learn and adapt their behavior through experience and training. The nervous system plays a vital role in facilitating the learning process and the formation of new neural connections.
When a dog learns a new behavior, such as sitting on command, the brain receives information about the desired action and sends signals through the nervous system to the relevant muscles. With repetition and reinforcement, these neural pathways become stronger, making the behavior more automatic and reliable.
3. Emotional responses:
The nervous system also influences a dog’s emotional responses. Just like humans, dogs experience a range of emotions, including joy, fear, anger, and sadness. These emotions are regulated by the limbic system, which is part of the brain’s emotional center.
When a dog encounters a situation that triggers an emotional response, such as meeting a new person or hearing a loud noise, the nervous system transmits signals that activate the appropriate emotional response. For example, if a dog feels threatened, the nervous system triggers the “fight or flight” response, leading to physiological changes such as increased heart rate and adrenaline release.
V. Common Nervous System Disorders in Dogs
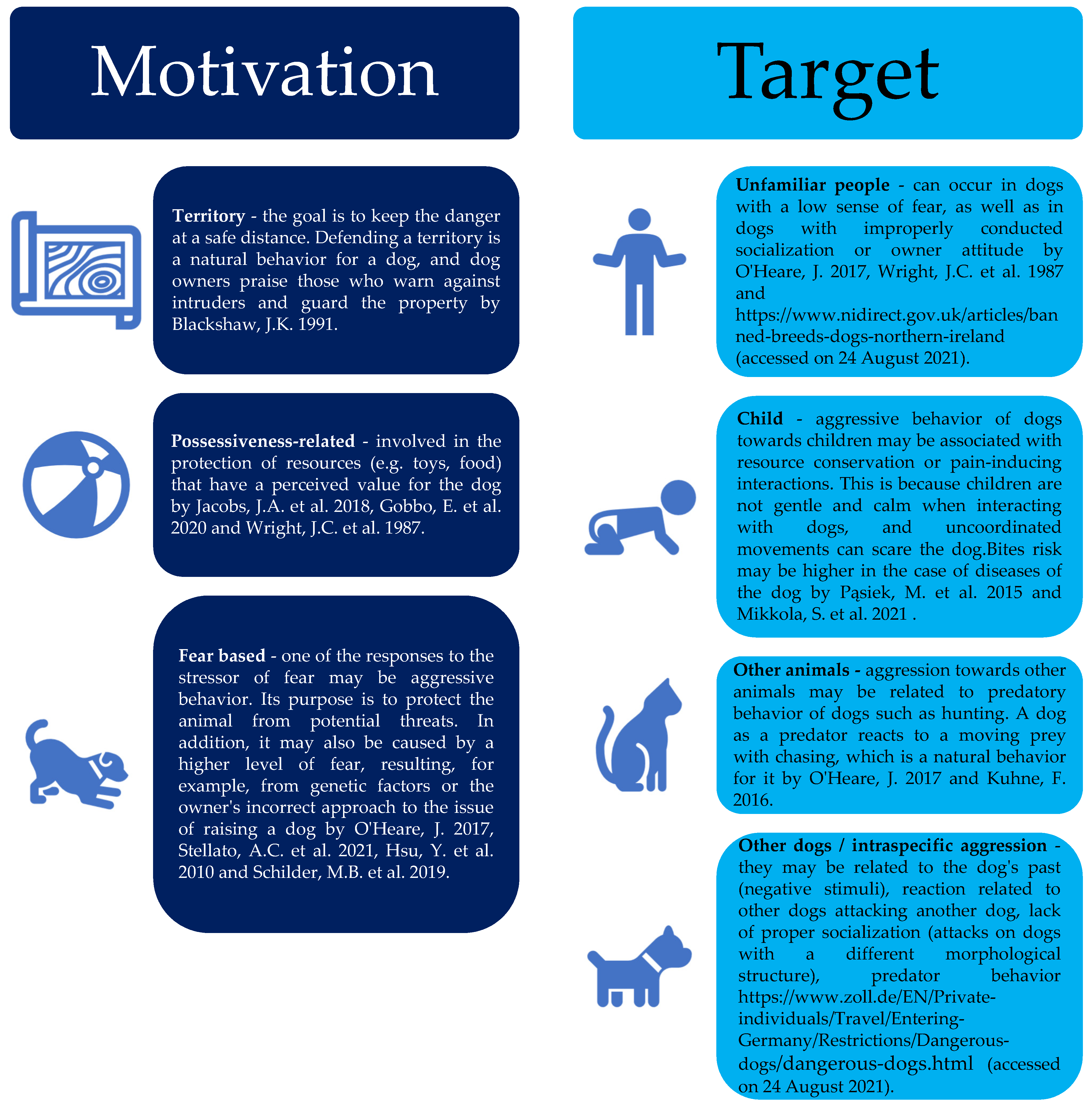
The nervous system plays a crucial role in controlling a dog’s behavior and movement. Unfortunately, just like humans, dogs can also experience various nervous system disorders that can affect their overall well-being. In this section, we will explore some of the most common neurological disorders in dogs, including epilepsy, canine cognitive dysfunction, and spinal cord injuries. We will also discuss the symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for these disorders.
A. Neurological disorders in dogs
1. Epilepsy: Epilepsy is a chronic neurological disorder characterized by recurrent seizures. It is one of the most common neurological conditions in dogs, affecting approximately 0.6% to 0.7% of the canine population. Epileptic seizures can vary in intensity and duration, and they can be triggered by various factors such as stress, excitement, or changes in the environment. While the exact cause of epilepsy in dogs is still unknown, it is believed to have a genetic component.
2. Canine cognitive dysfunction: Canine cognitive dysfunction, also known as doggy dementia, is a degenerative brain disorder that affects older dogs. It is similar to Alzheimer’s disease in humans and is characterized by a decline in cognitive function, memory loss, disorientation, and changes in behavior. The exact cause of canine cognitive dysfunction is not fully understood, but it is believed to be associated with the accumulation of abnormal proteins in the brain.
3. Spinal cord injuries: Spinal cord injuries can occur as a result of trauma, such as a car accident or a fall, or due to degenerative conditions like intervertebral disc disease. These injuries can lead to partial or complete loss of motor function and sensation below the site of the injury. Common symptoms of spinal cord injuries in dogs include paralysis, loss of bladder and bowel control, and pain. Treatment options for spinal cord injuries depend on the severity and location of the injury and may include surgery, medication, and physical therapy.
B. Symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for common nervous system disorders
Diagnosing nervous system disorders in dogs can be challenging, as the symptoms can vary depending on the specific condition and the individual dog. However, there are some common signs that may indicate a neurological problem, such as seizures, changes in behavior or personality, difficulty walking or standing, loss of coordination, and abnormal eye movements.
If you notice any of these symptoms in your dog, it is important to consult with a veterinarian for a proper diagnosis. The veterinarian will perform a thorough physical examination and may recommend additional tests, such as blood work, imaging studies (such as X-rays or MRI), or cerebrospinal fluid analysis, to determine the underlying cause of the symptoms.
The treatment options for common nervous system disorders in dogs depend on the specific condition and its severity. In the case of epilepsy, antiepileptic medications may be prescribed to control the seizures. Canine cognitive dysfunction can be managed through environmental enrichment, dietary supplements, and medications that help improve cognitive function. Spinal cord injuries may require surgical intervention, supportive care, and rehabilitation therapy to help the dog regain mobility and function.
In addition to medical treatment, it is important to provide a safe and supportive environment for dogs with nervous system disorders. This may include modifying the home environment to prevent accidents or injuries, providing mental stimulation and enrichment activities, and ensuring a balanced and nutritious diet.
VI. Training and Enrichment for a Healthy Nervous System in Dogs
Training and enrichment play a crucial role in maintaining a healthy nervous system in dogs. Just like humans, dogs need mental stimulation and exercise to keep their brains sharp and their cognitive functions intact. In this section, we will explore the importance of mental stimulation and exercise for a healthy nervous system, training techniques that promote brain health and cognitive function, and enrichment activities that engage the dog’s nervous system and prevent behavioral issues.
A. Importance of mental stimulation and exercise for a healthy nervous system
Mental stimulation and exercise are essential for dogs to maintain a healthy nervous system. Dogs are intelligent creatures that thrive on mental challenges and physical activities. When dogs are mentally stimulated, it keeps their brains active and helps prevent cognitive decline. Regular exercise also promotes the release of endorphins, which are natural mood enhancers that reduce stress and anxiety.
There are several ways to provide mental stimulation and exercise for dogs. One effective method is through interactive toys and puzzles. These toys require the dog to use their problem-solving skills to retrieve treats or solve a puzzle, keeping their minds engaged and active. Another way is through obedience training and agility exercises. Teaching dogs new commands and tricks not only stimulates their brains but also strengthens the bond between the dog and their owner.
Additionally, physical exercise is equally important for a healthy nervous system. Regular walks, runs, or play sessions help dogs release pent-up energy, maintain a healthy weight, and improve cardiovascular health. Exercise also promotes the production of neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine, which are essential for regulating mood and reducing stress.
B. Training techniques that promote brain health and cognitive function in dogs
Training techniques play a crucial role in promoting brain health and cognitive function in dogs. Positive reinforcement training is widely regarded as the most effective and humane method of training. This technique involves rewarding desired behaviors with treats, praise, or play, while ignoring or redirecting unwanted behaviors.
Positive reinforcement training not only strengthens the bond between the dog and their owner but also stimulates the dog’s brain. When dogs are rewarded for performing a desired behavior, it reinforces neural pathways in the brain, making it easier for them to repeat the behavior in the future. This type of training also encourages dogs to think and problem-solve, enhancing their cognitive abilities.
Another training technique that promotes brain health is clicker training. Clicker training involves using a small handheld device that makes a clicking sound when pressed. The clicker is paired with treats and used to mark desired behaviors. Dogs quickly learn to associate the sound of the clicker with a reward, making it an effective tool for training and shaping new behaviors.
C. Enrichment activities to engage the dog’s nervous system and prevent behavioral issues
Enrichment activities are essential for engaging the dog’s nervous system and preventing behavioral issues. Dogs are naturally curious and need mental stimulation to prevent boredom and destructive behaviors.
One popular enrichment activity is nose work. Dogs have an incredible sense of smell, and engaging their noses in scent-based activities can provide mental stimulation and keep them entertained. Hide treats or toys around the house or in the yard and let your dog use their nose to find them. This activity taps into their natural instincts and provides a fun and challenging experience for them.
Puzzle toys are another great way to engage the dog’s nervous system. These toys require the dog to solve a puzzle or manipulate objects to access treats or toys. They provide mental stimulation and keep the dog occupied for extended periods. There are various types of puzzle toys available, ranging from simple treat-dispensing toys to complex puzzle boards that require problem-solving skills.
Lastly, interactive play sessions with the owner or other dogs can provide both physical exercise and mental stimulation. Games like fetch, tug-of-war, or hide-and-seek engage the dog’s senses and keep them mentally and physically active. These activities also strengthen the bond between the dog and their owner, promoting a healthy and happy relationship.
VII. Nutrition and Supplements for Optimal Nervous System Function in Dogs
As a dog owner and enthusiast, I understand the importance of maintaining a healthy nervous system in our furry friends. The nervous system plays a crucial role in controlling behavior and movement, and ensuring its optimal function is essential for a happy and active dog. In this section, we will explore the essential nutrients for a healthy nervous system, the importance of a balanced diet in supporting nervous system health, and the supplements that can help support your dog’s nervous system.
A. Essential nutrients for a healthy nervous system
Just like humans, dogs require specific nutrients to support the health and function of their nervous system. These nutrients play a vital role in maintaining the integrity of nerve cells and promoting proper nerve transmission. Here are some essential nutrients that are beneficial for a healthy nervous system in dogs:
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Omega-3 fatty acids, such as EPA and DHA, are known for their anti-inflammatory properties and can help reduce inflammation in the nervous system. They can be found in fatty fish like salmon and sardines, as well as in fish oil supplements.
- Vitamin B complex: B vitamins, including B1 (thiamine), B6 (pyridoxine), and B12 (cobalamin), are essential for nerve function and can help support a healthy nervous system. Good sources of B vitamins include meat, fish, eggs, and whole grains.
- Vitamin E: Vitamin E is a powerful antioxidant that can help protect nerve cells from oxidative damage. It can be found in foods like nuts, seeds, and leafy green vegetables.
- Magnesium: Magnesium is involved in nerve transmission and can help promote a calm and balanced nervous system. It can be found in foods like spinach, pumpkin seeds, and almonds.
B. Importance of a balanced diet in supporting nervous system health
A balanced diet is essential for overall health and well-being, including the health of the nervous system. Providing your dog with a nutritious and well-rounded diet can help ensure they receive all the necessary nutrients to support their nervous system. Here are some key considerations for a balanced diet:
- High-quality protein: Protein is essential for the growth and repair of tissues, including nerve cells. Choose high-quality protein sources like lean meats, fish, and poultry.
- Healthy fats: Healthy fats, such as those found in fish, flaxseed, and olive oil, are important for brain health and can support a healthy nervous system.
- Complex carbohydrates: Complex carbohydrates, like whole grains and vegetables, provide a steady source of energy and can help support brain function.
- Fruits and vegetables: Fruits and vegetables are rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that can help protect nerve cells and support overall nervous system health.
It’s important to consult with your veterinarian to determine the specific dietary needs of your dog, as individual requirements may vary based on factors such as age, breed, and any underlying health conditions.
C. Supplements that can support the dog’s nervous system
In addition to a balanced diet, certain supplements can provide additional support to your dog’s nervous system. These supplements can help address specific issues or provide general support for optimal nervous system function. Here are some supplements that are commonly used to support the nervous system in dogs:
- Omega-3 fish oil: Omega-3 fish oil supplements can provide a concentrated dose of EPA and DHA, which are beneficial for reducing inflammation and supporting nerve health.
- Probiotics: Probiotics can help promote a healthy gut microbiome, which plays a crucial role in overall health, including nervous system function.
- Herbal remedies: Certain herbs, such as chamomile and valerian root, have calming properties and can help reduce anxiety and stress, promoting a balanced nervous system.
- Antioxidants: Antioxidant supplements, like vitamin E and CoQ10, can help protect nerve cells from oxidative damage and support overall nervous system health.
It’s important to note that while supplements can be beneficial, they should not replace a balanced diet. Always consult with your veterinarian before introducing any new supplements to your dog’s routine to ensure they are safe and appropriate for your pet.
By providing your dog with the essential nutrients they need, maintaining a balanced diet, and considering the use of supplements when necessary, you can help support their nervous system health and overall well-being. Remember, a healthy nervous system is essential for a happy and active dog!
